7.29 cross correlation; interaural cross correlation. Covariance of signals vs. time shift; i.e., the degree of similarity of a reference signal and a time-shifted signal, as a function of time shift or delay.
Annotation 1 The cross correlation is calculated as
where T is the observation period, and a(t) and b(t) are the respective signals.
Annotation 2 The coefficient of correlation varies from +1 (perfectly correlated; i.e., the two signals are identical), through zero (completely uncorrelated; i.e., the two signals are completely independent or orthogonal), to –1 (perfectly correlated, but with a complete 180° phase inversion between the signals).
Annotation 3 Auto correlation is the degree of similarity of a signal and a time-shifted version of itself.
Annotation 4 Interaural cross correlation describes the correlation between signals received at the two ears of a listener.
« Back to Standards Terminolgy Index
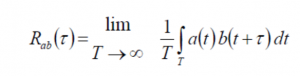

Recent Comments